Yield Multiplier
Overview
The yield multiplier strategy allows you to supercharge your on lending markets like Weft and Root Finance, allowing you to leverage your deposits, and increase your exposure to the asset, and APY, by (sometimes) over 5x!
Lending markets incentivize providing liquidity to their pools by rewarding those who do with yield. The yield multiplier strategy takes advantage of this by using flash loans, which are deposited into the pool alongside the user’s deposit, this increasing their exposure to the supplied asset. The value of the flash loan is then re-borrowed in another asset— with an interest rate lower than that of the deposit —and then repaid.
Risk
Your position in any given lending market has an attached risk (health) value, which indicates whether your deposit is worth more than your loans. The higher you leverage with the strategy, the more is borrowed in proportion to your supply. This means that even if the difference between the deposit and loan APYs is widely in favor of the deposit asset, you increase your risk of liquidations due to price fluctuations in the supply and debt assets, more so if they are volatile.
For more information see:
How it works
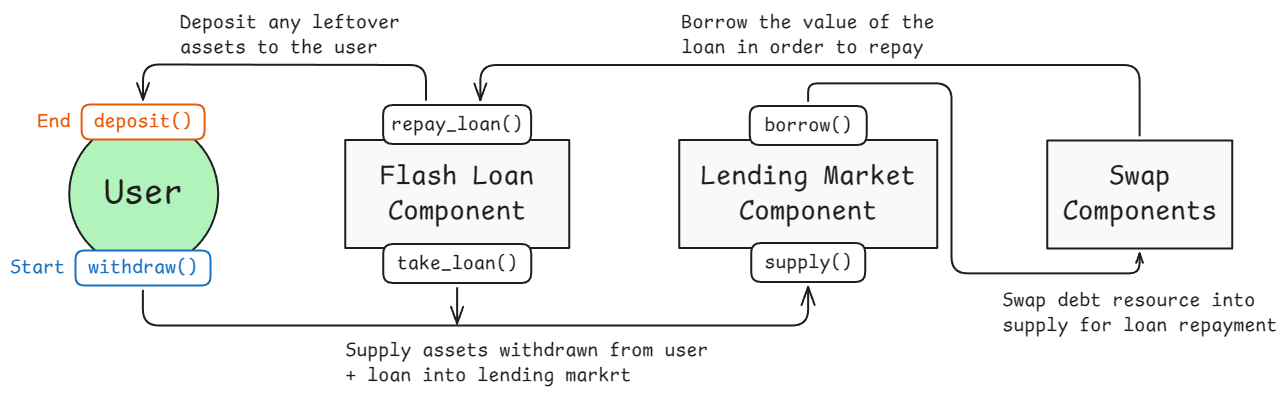
Opening an account within a Yield Multiplier cluster deposits a CDP (Collateralized Debt Position) from Weft or Root into the cluster. From there, in order to for the frontend to interact with it— e.g. deposit or withdraw assets —the start_execution and end_execution methods can be used, which allow any arbitrary interaction with the CDP, as long as it is returned to the cluster within the same transaction— see transient resources, and the GitHub for more info.
In order to enact the desired changes to the CDP— such as depositing 100XRD at 2x leverage —this general algorithm is used.
- Fetch current supply value () and debt value () of the CDP.
- Calculate the liquidity, . If , so risk , then a different algorithm is applied to put the CDP into a valid state.
- Get the product of user input (, can be or ) and liquidity,
- Calculate the new supply and debt values from the liquidity and leverage (),
- Calculate the change in supply and change in debt,
From and , different steps are applied depending on whether
- and
- and
- and
- and
as flash loans, supplying & borrowing, and withdrawing & repaying, have to be applied in differing configurations depending on the 4 outlined cases.
Configuration
These parameters are used when calculating the maximum leverage of a position.
| Protocol | Max. LTV | Max. Risk |
|---|---|---|
| WeftV2 | 0.95 | 0.95 |
| Root | 0.95 | 0.95 |
This is the fee configuration for the deployed clusters.
| Protocol | Supply | Debt | Open Fee | Execute Fee | Close Fee |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WeftV2 | xUSDC | xUSDT | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| WeftV2 | xUSDT | xUSDC | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| WeftV2 | xUSDT | XRD | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| WeftV2 | xUSDC | XRD | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| WeftV2 | xUSDT | xwBTC | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| WeftV2 | XRD | xETH | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| WeftV2 | xUSDT | xETH | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| WeftV2 | xUSDC | xETH | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| WeftV2 | xUSDC | xwBTC | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| Root | xUSDT | xETH | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| Root | xUSDT | LSULP | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| Root | xUSDT | XRD | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| Root | XRD | LSULP | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| Root | xUSDC | XRD | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| Root | xUSDT | xwBTC | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| Root | xUSDC | xETH | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| Root | xUSDC | LSULP | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| Root | xUSDC | xwBTC | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| Root | xUSDC | xwBTC | 16 | 4 | 4 |
Radix
Yield Multiplier - WeftV2
Package address:
package_rdx1phd58kfk9pyn5wny986tzwxsayfgs7dx4spq0shc29zcfj6cxgk3nx
Yield Multiplier - Root
Package address:
package_rdx1pkds3jnkp40x6yjs2mfzn4l3tkayjsmqf2xjs7qvq9zkwysyynqla5